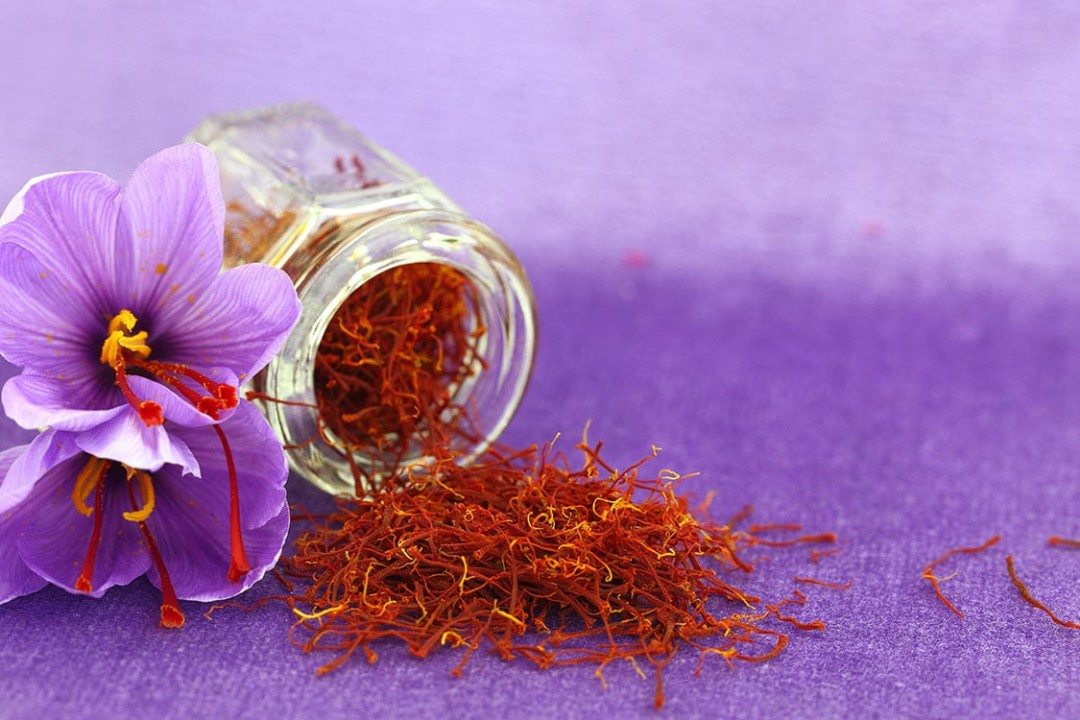

Saffron, often referred to as the “golden spice,” is one of the most expensive and prized agricultural products in the world. Known for its rich color, distinct flavor, and numerous health benefits, saffron is grown primarily in regions such as Iran, India, and Spain. However, the cultivation of saffron is a labor-intensive process that requires careful attention to environmental and economic sustainability. As global demand for this spice continues to rise, saffron buyers play an essential role in ensuring the sustainability of saffron cultivation.
1. Promoting Fair Trade and Ethical Sourcing
One of the primary ways saffron buyers can contribute to sustainability is by promoting fair trade practices. By establishing relationships with farmers that focus on fair wages, reasonable working conditions, and transparent trade agreements, buyers can help improve the livelihoods of saffron producers. For example, understanding the saffron price per kg in Afghanistan allows buyers to negotiate better deals that ensure farmers receive a fair price for their products. Ensuring that farmers are paid fairly encourages them to continue cultivating saffron and investing in sustainable farming practices. This helps create a more resilient saffron supply chain, where farmers are empowered and motivated to preserve their traditional farming techniques while adopting sustainable practices.
2. Supporting Environmentally-Friendly Farming Methods
Saffron cultivation is highly dependent on the local environment. Buyers can play a key role in encouraging farmers to use environmentally-friendly farming methods that reduce water usage, maintain soil health, and prevent the overuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Sustainable practices such as crop rotation, organic farming, and water conservation are essential for safeguarding the land for future generations. Buyers who actively seek out saffron produced using these methods are supporting the long-term sustainability of saffron cultivation and helping to mitigate the negative environmental impact of conventional farming practices.
3. Encouraging the Use of Technology and Innovation
Saffron buyers can also drive sustainability by supporting the adoption of innovative technologies in saffron farming. Technologies such as drip irrigation systems, automated harvesters, and soil sensors can help farmers optimize their cultivation processes, reduce waste, and increase productivity while using fewer resources. Buyers can collaborate with agricultural tech companies to introduce these innovations to saffron producers, ensuring that cultivation practices become more efficient and sustainable.
4. Strengthening Community Involvement
Sustainability is not just about the environment or economics; it’s also about the community. Saffron buyers who invest in local communities, including training and educating farmers on sustainable farming practices, help create a more sustainable supply chain. Buyers can encourage cooperatives and community groups to work together to improve production practices, share knowledge, and ensure that local farmers continue to thrive.
conclusion
In conclusion, saffron buyers are instrumental in ensuring the sustainability of saffron cultivation. Through ethical sourcing, support for environmentally-friendly farming methods, adoption of technology, and strengthening community involvement, buyers can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient saffron industry. Their efforts help safeguard the future of saffron production for generations to come while meeting the growing global demand for this precious spice.




Leave a Reply