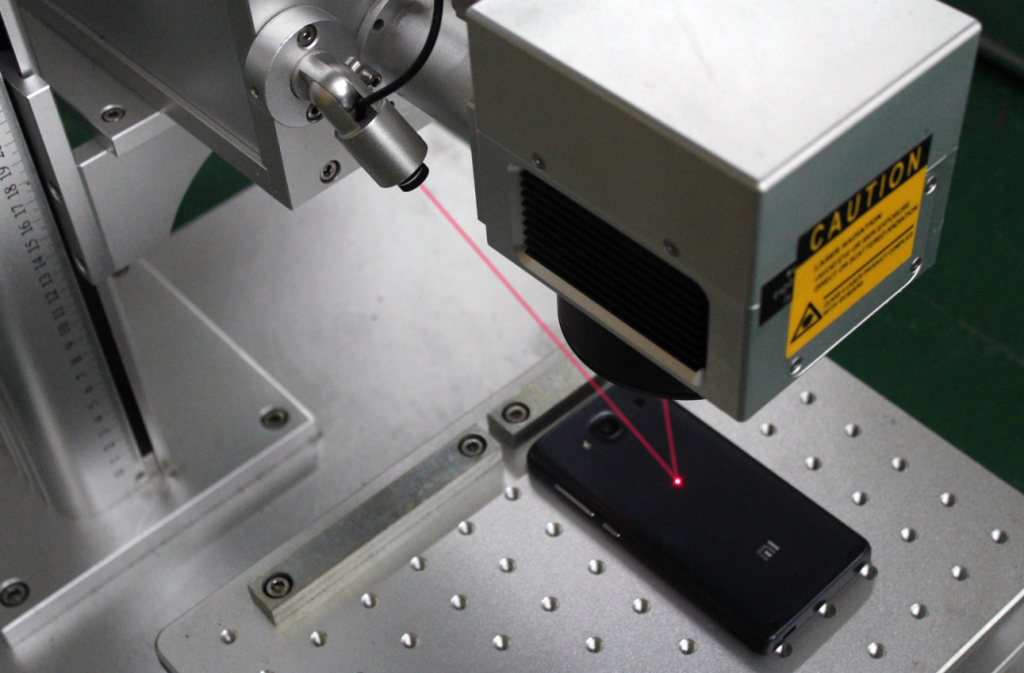
Laser machine marking is a non-contact method used to create precise and permanent markings on various materials. This process relies on focused laser beams to alter the surface of a material, leaving behind text, images, barcodes, or intricate designs. Unlike traditional engraving or etching, laser machine marking does not require physical contact with the material, which ensures high accuracy and consistency.
The Science Behind Laser Machine Marking
The core principle of laser machine marking is the interaction between a concentrated beam of light and the material’s surface. When the laser beam comes into contact with the material, it triggers a reaction such as oxidation, discoloration, or material removal, depending on the type of marking method used.
The laser beam is generated from a source such as fiber, CO₂, or UV lasers, depending on the material being marked. This beam is directed through a set of mirrors and lenses, which help to focus it onto the target area. The high-energy laser alters the material’s properties, leaving a permanent mark that is resistant to wear, heat, and chemicals.
Why No Physical Contact is Required
Laser machine marking relies on light energy rather than mechanical force. Traditional methods like engraving use physical tools to carve markings into a surface, which can cause wear and tear on both the tool and the material. In contrast, laser marking is a controlled energy transfer process where the laser beam interacts with the material at a microscopic level.
Since there is no direct contact, there is no risk of material deformation or damage. The laser system moves with high precision, ensuring that even intricate designs or small text remain sharp and legible.
Types of Laser Machine Marking Methods
Different materials and applications require specific laser marking techniques. Some of the most common methods include:
1. Annealing Marking
This technique is primarily used for metals, where the laser heats the surface to create an oxidation layer. This results in a high-contrast, black or dark-colored mark without removing any material.
2. Carbon Migration
In this process, the laser alters the material composition by redistributing carbon elements, creating a darkened mark. This is commonly used for metals and alloys.
3. Color Marking
Some laser machines can produce colored marks on stainless steel and titanium by controlling the heat applied to the surface. This allows for aesthetic and decorative applications.
4. Surface Etching
A shallow yet permanent mark is created by slightly removing the surface layer of the material. This method is widely used in industrial and manufacturing settings.
5. Foaming
Mostly used on plastics, this process creates raised marks by heating the surface and forming bubbles in the material. The resulting marks are typically lighter in color than the original material.
6. Engraving
Although often confused with marking, engraving is a deeper process where the laser removes layers of material to create a more pronounced, permanent impression.
Applications of Laser Machine Marking
Laser marking is widely used across various industries due to its precision and durability. Some common applications include:
- Medical Industry – Marking surgical instruments and medical devices with tracking codes and serial numbers.
- Aerospace and Automotive – Engraving part numbers, barcodes, and safety labels on aircraft and car components.
- Electronics – Creating circuit board markings and serial numbers for traceability.
- Jewelry and Luxury Goods – Engraving intricate designs, serial numbers, and brand logos.
- Industrial Manufacturing – Marking tools, machinery, and mechanical parts with permanent identification codes.
Factors Affecting the Quality of Laser Machine Marking
Several factors determine the accuracy and clarity of a laser-marked design, including:
1. Laser Power
The intensity of the laser beam must be adjusted based on the material type to avoid excessive heat damage or incomplete marking.
2. Wavelength
Different materials respond to different laser wavelengths. Fiber lasers are ideal for metals, while CO₂ lasers work well on organic materials like wood and plastics.
3. Speed of Marking
Faster marking speeds can lead to shallower marks, while slower speeds allow for deeper engraving or darker marks.
4. Focal Point Adjustment
Proper focusing ensures that the laser delivers maximum energy to the surface, resulting in sharp and high-contrast marks.
5. Material Composition
Metals, plastics, and ceramics react differently to laser exposure, requiring precise calibration to achieve the desired results.
Laser Machine Marking vs. Traditional Marking Techniques
Unlike stamping, chemical etching, or mechanical engraving, laser machine marking offers a more efficient and environmentally friendly solution. Traditional methods often require consumables like inks, acids, or cutting tools, whereas laser marking operates cleanly with minimal waste.
Additionally, laser-marked surfaces retain their integrity over time, resisting fading, corrosion, or wear, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term traceability.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Laser marking is a safe and sustainable marking method compared to chemical-based or mechanical alternatives. It produces no toxic fumes, requires no consumable materials, and generates minimal waste. However, safety measures such as proper ventilation, protective eyewear, and enclosure systems should be implemented to protect operators from laser exposure.
Future Trends in Laser Machine Marking
The laser marking industry continues to evolve with advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and high-speed processing. Some emerging trends include:
- AI Integration – Smart laser systems with AI-driven quality control for enhanced precision.
- Faster Marking Speeds – Development of ultra-fast laser sources for high-volume production.
- Eco-Friendly Solutions – Energy-efficient laser systems with lower power consumption.
- 3D Laser Marking – The ability to mark curved and irregular surfaces with high accuracy.
Conclusion
Laser machine marking is a highly efficient, precise, and durable process that eliminates the need for physical contact while ensuring permanent markings on a variety of materials. By using concentrated laser energy, this technique provides long-lasting identification without damaging the surface. Industries worldwide rely on laser machine marking for traceability, branding, and product identification, making it a crucial technology for modern manufacturing.





Leave a Reply