High levels of prolactin, a hormone primarily responsible for stimulating milk production in breastfeeding women, can lead to significant health risks when its levels become abnormally elevated. This condition, known as hyperprolactinemia, can affect various aspects of an individual’s health, ranging from reproductive function to bone density. One of the most concerning health risks of high prolactin is bone loss, which can lead to osteoporosis and fractures. Fortunately, treatments like Dostinex, a dopamine agonist, are effective in reducing prolactin levels, thereby mitigating these health risks.
What is prolactin?
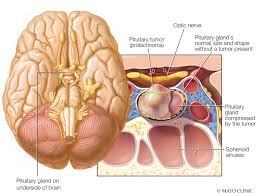
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain. Its primary role is to promote milk production in the mammary glands during and after pregnancy. In addition to its role in reproduction, prolactin has secondary effects on other bodily functions, such as regulating the immune system and influencing the development of certain behaviors.
While prolactin is essential for lactation, its levels need to remain within a normal range. Elevated prolactin levels can occur for various reasons, including pituitary tumors (prolactinomas), medications, hypothyroidism, and stress. In some cases, the cause may remain unknown.
Causes of High Prolactin Levels
High prolactin levels can be caused by various factors, including:
- Pituitary Tumors (Prolactinomas): These benign tumors of the pituitary gland are the most common cause of hyperprolactinemia.
- Medications: Certain medications, including antipsychotics, antidepressants, and antinausea drugs, can interfere with dopamine production or action, leading to an increase in prolactin levels.
- Hypothyroidism: Low thyroid hormone levels can cause the pituitary gland to produce more prolactin.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Prolactin levels naturally rise during pregnancy and breastfeeding. However, if prolactin remains elevated postpartum, it may indicate a problem.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can lead to an increase in prolactin production.
Health Risks of High Prolactin Levels
When prolactin levels are elevated beyond the normal range, they can cause a range of health problems, including:
1. Bone Loss (Osteoporosis)
One of the most serious health risks associated with high prolactin levels is bone loss. Prolactin plays a role in the regulation of bone metabolism, and when its levels are elevated for an extended period, it can disrupt the balance between bone formation and resorption, leading to decreased bone density. This condition is particularly concerning for women, especially those who are postmenopausal or have undergone early menopause, as they are already at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis.
Chronic high prolactin levels can lead to:
- Increased Bone Resorption: Prolactin can stimulate the activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for breaking down bone tissue. This leads to increased bone resorption and a reduction in bone density.
- Reduced Bone Formation: Elevated prolactin can also inhibit osteoblast activity, reducing the production of new bone tissue. This imbalance contributes to bone thinning and increases the risk of fractures.
- Fractures and bone fragility: As bone density decreases, bones become more fragile and susceptible to fractures, even with minor trauma.
2. Milk Production in Non-Lactating Individuals
While prolactin is essential for milk production during pregnancy and breastfeeding, elevated levels of the hormone in non-lactating women and men can lead to inappropriate milk production, a condition known as galactorrhea. This abnormal milk production can occur without the usual triggers (pregnancy or breastfeeding) and may be accompanied by breast tenderness or swelling.
In men, high prolactin can also lead to a condition called gynecomastia, which is the development of enlarged breast tissue. Both conditions can lead to psychological distress, including embarrassment and body image issues.
3. Reproductive Issues
High prolactin levels can also interfere with reproductive health. In women, elevated prolactin can lead to:
- Menstrual Irregularities: High prolactin levels can disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular periods or even a complete absence of menstruation (amenorrhea).
- Infertility: Prolactin inhibits the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which is essential for ovulation. This can make it difficult for women to conceive.
In men, elevated prolactin can cause:
- Reduced Testosterone Levels: High prolactin can suppress testosterone production, leading to symptoms such as erectile dysfunction, reduced libido, and infertility.
- Decreased Sperm Count: Elevated prolactin can affect sperm production, reducing sperm count and motility, which can lead to fertility issues.
4. Headaches and Vision Problems
When high prolactin levels are caused by a prolactinoma (a pituitary tumor), the tumor may grow large enough to press on surrounding structures, such as the optic nerves. This can cause symptoms like:
- Headaches: Chronic, persistent headaches are common with prolactinomas.
- Vision Impairment: If the tumor presses on the optic nerves, it can lead to visual disturbances or even permanent vision loss if left untreated.
Treatment for High Prolactin: Cabergoline
The treatment for high prolactin levels primarily focuses on reducing the production of prolactin, often through the use of dopamine agonists like cabergoline. Cabergoline works by stimulating dopamine receptors in the brain, which inhibits prolactin secretion from the pituitary gland.
1. Cabergoline: Mechanism of Action
Cabergoline is a potent and selective dopamine D2 receptor agonist. By activating these receptors in the brain, cabergoline suppresses prolactin production and secretion from the pituitary gland. This helps normalize prolactin levels and reverse the symptoms associated with hyperprolactinemia.
2. Dosage of Cabergoline
Cabergoline is typically available in tablet form, with doses ranging from 0.25 mg to 1 mg per tablet. For the treatment of hyperprolactinemia, the following dosages are commonly prescribed:
- Cabergoline 0.25 mg: Cabergoline 0.25 mg is usually the starting dose for most patients. It may be increased gradually depending on the patient’s response to treatment.
- Cabergoline 0.5 mg: For patients requiring a higher dose, Cabergoline 0.5 mg may be prescribed. Cabergoline 0.5 mg is often the standard dosage for reducing prolactin levels effectively.
- Cabergoline 1 mg: In some cases, a higher dose of Cabergoline may be required. However, doses of 1 mg or more are typically used in more severe cases.
Patients are usually advised to take cabergoline twice a week, and the dosage may be adjusted based on the individual’s response and tolerance to the medication.
3. Benefits of Cabergoline
- Reduction in Prolactin Levels: The primary benefit of cabergoline is its ability to reduce prolactin levels, which can alleviate symptoms such as galactorrhea, menstrual irregularities, and infertility.
- Restoration of Normal Hormonal Balance: By lowering prolactin, cabergoline helps restore the hormonal balance necessary for normal reproductive function.
- Bone Protection: By normalizing prolactin levels, cabergoline can help prevent the bone loss associated with high prolactin, thus reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Improved Quality of Life: By alleviating symptoms such as inappropriate milk production, headaches, and vision problems, cabergoline can significantly improve a patient’s overall quality of life.
4. Possible Side Effects of Cabergoline
While cabergoline is generally well-tolerated, it may cause side effects in some individuals, including:
- Nausea and vomiting: These are common side effects, especially when starting treatment.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Some patients may experience dizziness, particularly when standing up quickly.
- Fatigue: Some individuals may feel unusually tired or drowsy.
- Heart Valve Issues: Long-term use of cabergoline may be associated with an increased risk of heart valve problems, so patients should be monitored regularly by their healthcare provider.
Conclusion
High prolactin levels, whether caused by pituitary tumors or other factors, can have a significant impact on an individual’s health, particularly with regards to bone loss and reproductive issues. Treatment with dopamine agonists like Cabergoline offers a highly effective solution for normalizing prolactin levels, reducing symptoms, and preventing long-term complications such as osteoporosis. If you are experiencing symptoms of hyperprolactinemia, consult a healthcare provider to discuss treatment options, including cabergoline, to restore your hormonal balance and improve your overall well-being.





Leave a Reply